If you take one thing away from this slide, memorize this: Trusted Computing allows a piece of data to dictate what Operating System and Application must be used to open it.
According to Wikipedia:
Trusted computing involves five features:
This, like many other descriptions of Trusted Computing, hides the underlying principle. Study our diagram below instead.Trusted computing in one picture:
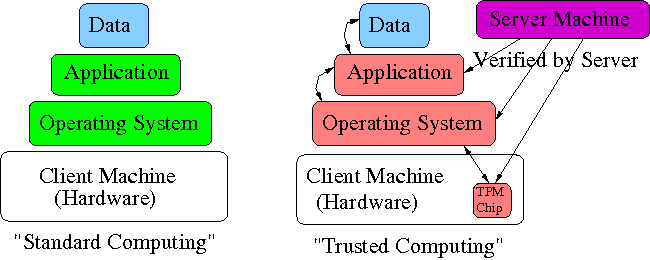
Trusted computing in one sentence:
Trusted Computing allows a piece of data to dictate what Operating System and Application must be used to open it. Ponder on this.In current situations, given a piece of data, you can choose what OS and what application you use to open it (though some do not make practical sense). Under Trusted Computing, the data dictates what Operating System and Application must be used to access it.
TPM Unit:
 |
|
What Trusted Computing Provides
Sealed Storage
Pieces of data can be 'sealed', ensuring that only certain pieces of software (chosen by a third party, not you) can unseal and interact with the data. These software, designed by the third party, can be designed to limit/control the way the user interacts with the data.From a technical standpoint, this is done through encryption and verifying the software/operating system stack before decrypting.
We can think of Sealed Storage as Remote Attestation without an outside server.
