|
sym-ildl
1.2
Incomplete LDL' factorizations of indefinite symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices.
|
|
sym-ildl
1.2
Incomplete LDL' factorizations of indefinite symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices.
|
sym-ildl is a C++ package for solving and producing fast incomplete factorizations of symmetric indefinite or skew-symmetric matrices. Given an  symmetric indefinite or skew-symmetric matrix
symmetric indefinite or skew-symmetric matrix 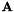 , this package produces an incomplete
, this package produces an incomplete  factorization. Prior to factorization, sym-ildl first scales the matrix to be equilibrated in the max-norm [2], and then preorders the matrix using either the Reverse Cuthill-McKee (RCM) algorithm or the Approximate Minimum Degree algorithm (AMD) [1]. To maintain stability, the user can use Bunch-Kaufman or rook partial pivoting during the factorization process. The factorization produced is of the form
factorization. Prior to factorization, sym-ildl first scales the matrix to be equilibrated in the max-norm [2], and then preorders the matrix using either the Reverse Cuthill-McKee (RCM) algorithm or the Approximate Minimum Degree algorithm (AMD) [1]. To maintain stability, the user can use Bunch-Kaufman or rook partial pivoting during the factorization process. The factorization produced is of the form
![\[ \mathbf{P^{T}SASP \approx LDL^{T}}. \]](form_3.png)
where 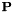 is a permutation matrix,
is a permutation matrix, 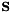 a scaling matrix, and
a scaling matrix, and  and
and  are the unit lower triangular and block diagonal factors respectively. The user can also optionally solve the given linear system, using sym-ildl's incomplete factorization to precondition the built-in solver or using the full factorization as a direct solver.
are the unit lower triangular and block diagonal factors respectively. The user can also optionally solve the given linear system, using sym-ildl's incomplete factorization to precondition the built-in solver or using the full factorization as a direct solver.
This package is based on and extends an incomplete factorization approach proposed by Li and Saad [3] (which itself builds on Li, Saad, and Chow [4]).
[Latest release: 11/15/2015]
To begin using the package, first download the files above or compile the code hosted at https://github.com/inutard/matrix-factor. The GitHub repository contains the most up to date source code as well as an "experimental" branch that we release new features to. The package works under most Unix distributions as well as Cygwin under Windows. The default compiler used is g++, simply type make at the command line to compile the entire package. In addition to usage as a standalone program, the package also has a Matlab interface.
For using sym-ildl as a software library, see the API here. sym-ildl is a header only library, so one only needs to include source/solver.h for everything to work.
The compiled program ldl_driver takes in through the command line one parameter (the matrix) as well as several additional optional parameters.
The format of execution is:
The parameters can be given in any order, and will use a default value when not specified.
A description of each of these parameters can be accessed by typing
Generally speaking, the code operates in two phases: generating the preconditioner (factorization) and solving the linear system (solver). The factorization parameters can be used to specify how the LDL' preconditioner is built. If a right hand side is specified, the built-in solver attempts to solve the given linear system. The solver takes the preconditioner and uses it in either preconditioned MINRES or a direct solve (full factorization with Bunch-Kaufman or rook pivoting).
For convenience, the parameters are listed below.
| filename | The filename of the matrix to be loaded. Several test matrices exist in the test_matrices folder. All matrices loaded are required to be in matrix market (.mtx) form. |
| fill | Controls memory usage. Each column of  is guaranteed to have fewer than is guaranteed to have fewer than  elements. Each column of elements. Each column of  has at most 2 elements. When this argument is not given, the default value for has at most 2 elements. When this argument is not given, the default value for fill is 3.0. |
| tol | Controls agressiveness of dropping. In each column k, elements less than 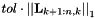 are dropped. The default value for are dropped. The default value for tol is 0.001. |
| pp_tol | A parameter to aggressiveness of Bunch-Kaufman pivoting (BKP). When pp_tol is 0, there is no partial pivoting. Values between 0 and 1 vary the number of pivots of BKP makes. When pp_tol is equal to 1, standard BKP is used. The pp_tol parameter is ignored if the pivot parameter is set to 'rook'. See the pivot parameters for more details. The default is 'rook'. |
| reordering | Determines what sort of preordering will be used on the matrix. Choices are 'amd', 'rcm', and 'none'. The default is 'amd'. |
| inplace | Indicates whether the factorization should be performed in-place, leading to roughly a 33% saving in memory. This memory comes out of extra information used in the solver. If the solver is needed, then inplace should not be used. y indicates yes, n indicates no. The default flag is n. |
| pivot | Indicates the pivoting algorithm used. Choices are 'rook' and 'bunch'. If rook is used, the pp_tol parameter is ignored. The default is 'rook'. |
| save | Indicates whether the output matrices should be saved. y indicates yes, n indicates no. The default flag is y. All matrices are saved in matrix market (.mtx) form. The matrices are saved into a folder named output_matrices. There are five saved files: outA.mtx, outL.mtx, outD.mtx, outS.mtx, and outP.mtx. outB.mtx is the matrix 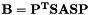 . The rest of the outputs should be clear from the description above. . The rest of the outputs should be clear from the description above. |
| display | Indicates whether the output matrices should be displayed to the command line, used for debugging purposes. y indicates yes, n indicates no. The default flag is n. For this parameter to appear, sym-ildl must be compiled with SYM_ILDL_DEBUG defined. |
| solver | This chooses the solver for sym-ildl if given a right hand side. The options are 'sqmr', 'minres', 'full', and 'none'. If the 'full' solver is chosen, the full factorization is produced and a straightforward direct solve is done. Setting this parameter to y overrides all other solver parameters as well as -fill and -tol (since we will no longer produce an incomplete factorization). The default solver is 'sqmr'. |
| max_iters | Number of iterations that the builtin iterative solvers (SQMR or MINRES) can use. The default is -1 (i.e. iterative solver is not applied). The output solution is written to output_matrices\outsol.mtx. |
| solver_tol | Relative tolerance for the builtin iterative solvers. When the iterate x satisfies ||Ax-b||/||b|| < solver_tol, the iterative solver is terminated. The default is 1e-6. |
| rhs_file | The filename of the right hand size we want to solve. All right hand sides loaded are required to be in matrix market (.mtx) form. If no right hand sides are given, only the preconditioner is generated. |
pivot, equil, and reordering parameters are best left to the default options.aug3dcqp matrix stored in test_matrices/aug3dcqp.mtx. Using the parameters described above, the execution of the program may go something like this: aug3dcqp.mtx matrix (fill=3.0, tol=0.001) from the test_matrices folder and saves the outputs. The time it took to pre-order and equilibrate the matrix (0.047s) as well as the actual factorization (0.109s) are also given.-fill=3.0 -tol=0.001 -reordering=amd -save=y. In general, we may give ldl_driver the arguments in any order, and omit any number of them (except the filename argument).rhs_file argument) and a maximum number of solver iterations. When no right hand side is specified (but a solver iteration is), sym-ildl assumes a right hand side of all 1's for debugging purposes: If everything is compiled correctly, simply open MATLAB in the package directory. The startup.m script adds all necessary paths to MATLAB upon initiation. The program can now be called by its function handle, ildl.
ildl takes in seven arguments, six of them being optional. A full description of the parameters can be displayed by typing
For convenience, the parameters are described below:
| A | The matrix to be factored. |
| fill | Controls memory usage. Each column is guaranteed to have fewer than  elements. When this argument is not given, the default value for elements. When this argument is not given, the default value for fill is 3.0. |
| tol | Controls aggressiveness of dropping. In each column k, elements less than 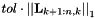 are dropped. The default value for are dropped. The default value for tol is 0.001. |
| reordering | Determines what sort of pre-ordering will be used on the matrix. Choices are 'amd', 'rcm', and 'none'. The default is 'amd'. |
| equil | Determines if matrix is to be equilibriated (in the max norm) before anything. This parameter must be one of 'bunch' or 'none'. Default: 'bunch' |
| pivot_type | Chooses the pivoting scheme used during the factorization. This parameter must be one of 'rook' or 'bunch'. Tbe default is 'rook'. |
| pp_tol | Threshold parameter for Bunch-Kaufman pivoting (BKP). When pp_tol >= 1, full BKP is used. When pp_tol is 0, there is no partial pivoting. As pp_tol increases from 0 to 1, we smoothly switch from no pivoting to full BKP. Low values of pp_tol can be useful as an aggressive pivoting process may damage and permute any special structure present in the input matrix. The default value is 1.0. When rook pivoting is used, this parameter has no effect. |
As with the standalone executable, the function has five outputs: L, D, p, S, and B:
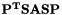 .
. 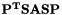 .
. 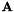 .
.  in the max-norm.
in the max-norm. 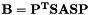 after factorization.
after factorization.A generated is a special type of matrix called a saddle-point matrix. These matrices are indefinite and arise often in optimzation problems. Note that A must be a MATLAB sparse matrix.ildl with the parameters described above: ildl will supply some timing information to the console when used. The reordering time is the time taken to equilibrate and pre-order the matrix. The factorization time is the time it took to factor and pivot the matrix with partial pivoting.ildl only one parameter: fill=3.0, tol=0.001, pivot_type='rook', pp_tol=1.0, and reordering=amd are used.To use the factorization as a preconditioner, we must apply the permutation and scaling matrices returned by ildl. For convenience here is a complete example of how ildl can be used with GMRES:
When the matrix is skew-symmetric, almost all documentation above still applies. The only difference is that the executable is skew_ldl_driver instead of ldl_driver. The skew functionality of sym-ildl can be found in the experimental branch of https://github.com/inutard/matrix-factor.
Let's factor the m3dskew50 matrix stored in test_matrices/skew/m3dskew50.mtx. As before, this is as simple as:
As in the symmetric case, we used the default values for the parameter we did not specify. A description of each of these parameters can be accessed by typing
Within MATLAB, using sym-ildl is even easier. As in the symmetric case, the command ildl can be used. Everything remains the same as the symmetric case, as ildl automatically detects whether the input is symmetric or skew-symmetric.
Let's first generate a skew-symmetric matrix for testing:
Since B is a matrix of random values between 0 and 1, A is almost certainly non-singular. Now we can call ildl exactly as before:
Finally, helpful information on the parameters for ildl can be found by typing:
sym-ildl is open source, and we're always looking for new contributions! The entire codebase is freely accessible at https://github.com/inutard/matrix-factor. We also use the MIT Licence, which essentially allow free use of this software in any way you want (see here for more details). Simply send us a pull request on GitHub to contribute.
If you have found our code useful, please consider citing us! A technical report (pdf), a BibTeX entry, and a link to the code are available here:
SYM-ILDL: Incomplete LDL^{T} Factorization of Symmetric Indefinite and Skew-Symmetric Matrices. Chen Greif, Shiwen He, Paul Liu. UBC Computer Science Technical Report, 2016. [pdf] [bib]
 1.8.11
1.8.11